Web 3.0

Over the past twenty years, the Internet has changed considerably. At the beginning, we were simply using the Internet Relay Chat (IRC) to communicate with other people. Nowadays we got plenty of other applications, which made the Internet an essential part of human interaction and connectivity, and it keeps evolving. Modern social media platforms, digital payments through sophisticated online banking services, cryptocurrency and blockchain are participating to this evolution. So far, we have used Web 1.0 and 2.0, but what exactly should we expect from Web 3.0? Let us dive into the Web’s history to understand its technological progress.
History of the web: From web 1.0 to web 3.0
Web 1.0 (1990-2004):
The web 1.0 is the earliest version of the Internet. Tim Barnes Lee is the creator of this version. He had the idea to create it to solve an issue his colleagues were facing: sharing information from one computer to another was complicated. At that time, the process consisted of using floppy and hard disks to transfer information. Tim wanted then to simplify this process: connecting all computers so that all information was available through a webpage for all users.
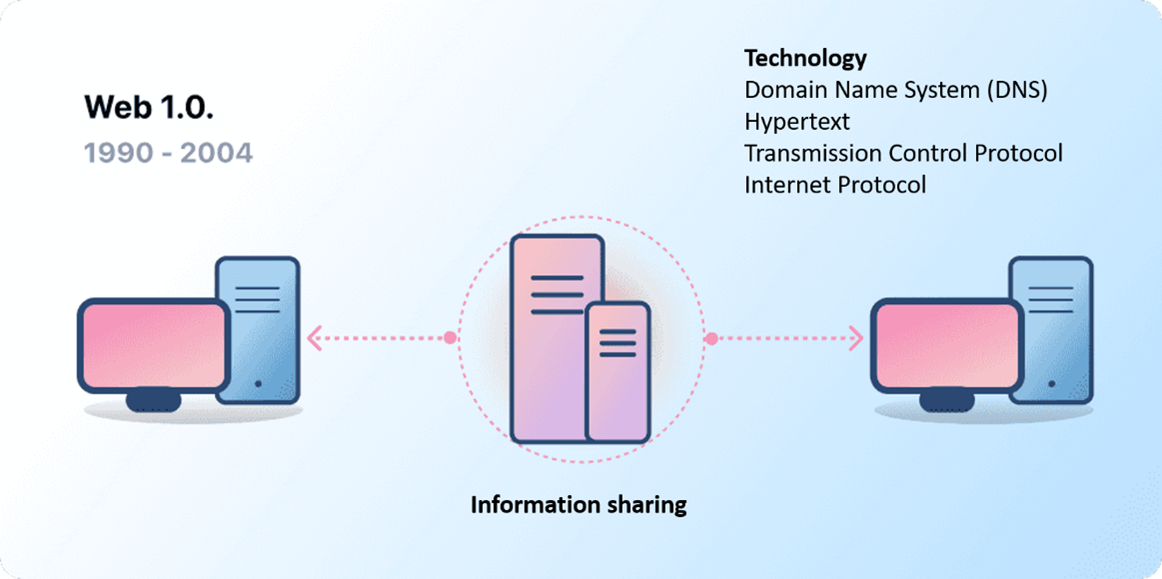
To complete this process, he used an addressing system, the Internet Protocol (IP), which allows each computer to be identified by their numeric addresses. Sharing information amongst all computers became easy, as it was possible to locate the address of any computer. He also created a system called Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) that controls how information moves from a computer to another. There was no way for users to edit data or upload their own. Social interactions were limited to simple chat messaging and forums.
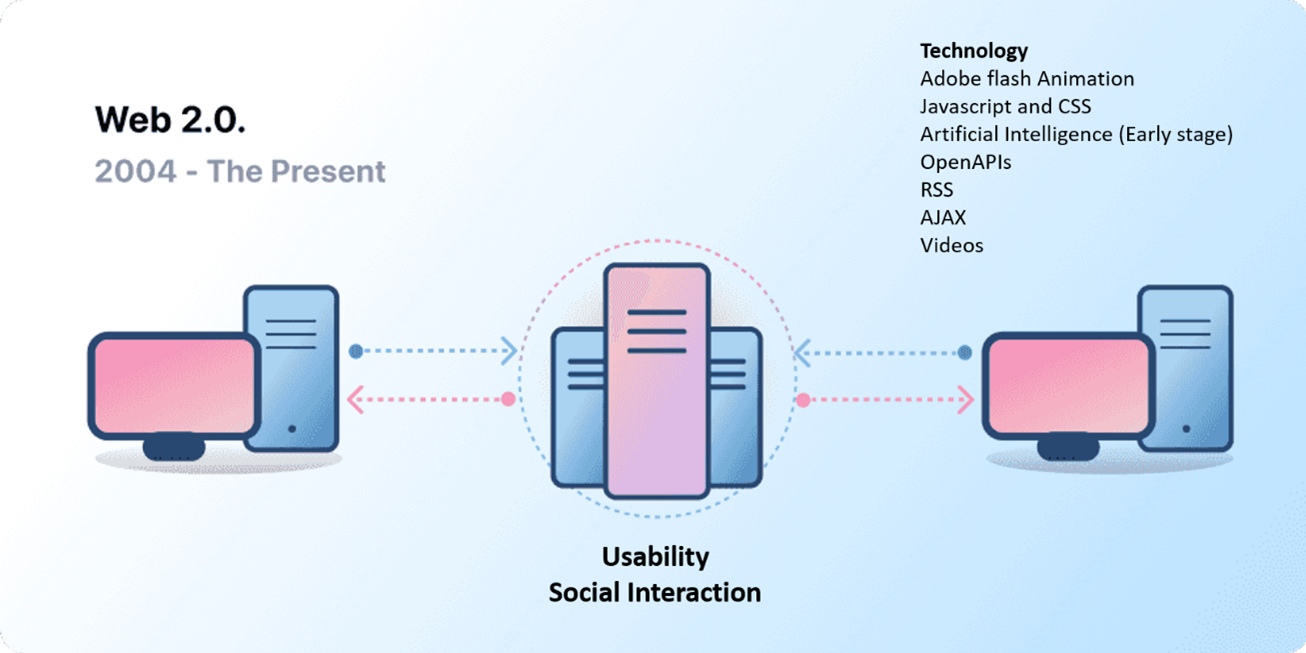
Web 2.0 (2004-Now)
In the late 1990s, a shift to a more interactive Internet began to take shape. With Web 2.0, users were able to interact with websites via databases, server-side processing, forms, and social networks. These tools shifted the web experience from a static to a dynamic state.
Web 2.0 enabled multiple collaborations between users, service companies and organizations that are using and storing our data to improve the quality and diversity of services. With the rising amount of data, Web 2.0 brought in some challenges we had not seen before. As more people are coming online and with the rising amount of data shared, nowadays we are facing data privacy and data security challenges as users do not own their information nor control where the information goes and who has access to it.
Web 3.0 (Now-Future)
The Web 3.0 (also known as Web3) is the next generation of Internet technology that relies heavily on machine learning, artificial intelligence (AI) and blockchain technology (see our article on the blockchain). The term was coined by Gavin Wood, founder of Polkadot and co-founder of Ethereum. In contrast with Web 2.0 where it focuses on user-created content hosted on centralized websites, Web 3.0 will give users more control over their online data.
This movement aims to create open, connected and intelligent websites and web applications through better machine understanding of data. Decentralization and digital economies also play an important role in Web 3.0, as they allow us to assign value to content created.

How does it work?
Web 3.0 aims to deliver personalized and relevant information faster using AI and advanced machine-learning techniques. Intelligent search algorithms and development of Big Data analytics means that machines can intuitively understand and recommend content. Web 3.0 will also focus on content ownership and support for user-accessible digital economies. Just look at YouTube or Netflix to see the power of algorithms and the improvements they have already made.
Key characteristics of Web 3.0
Web 3.0 is still far from being fully embraced, but its core concepts are mostly already defined.
There are four topics listed as the most important aspects of the future of Web 3.0:
Semantic web
Over time, machines have improved their ability to understand data and content created by humans. However, creating a fluid experience where semantics are fully understood will take time. For example, the use of the word “bad” can, in some cases, mean “good”. To a machine, this can be incredibly difficult to understand. However, with Big Data and more information to study, AI is beginning to better understand meanings and emotions, enhancing user experience and facilitating connectivity.
Blockchain and cryptocurrency
Blockchain and cryptocurrency have great potential when it comes to Web 3.0. Decentralized networks are successfully creating incentives for more responsible data ownership, governance, and content creation.
3D Graphics and Spatial Web
The look of the web will change dramatically. We are already seeing a transition to 3D environments that even incorporate virtual reality. The metaverse (see our Headmind blog article) is one of the pioneers of these experiences, and we are already familiar with encounters through 3D video games. The fields of user interface and user experience are also enabling information to be presented in a more intuitive way for web users.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence is the key to turning human-created content into machine-readable data. We already know about customer service robots, but that is just the beginning. AI can present us with data and sort it, making it a versatile tool for Web 3.0. Best of all, AI will learn and improve itself, reducing the work required for human development in the future.

What makes Web 3.0 superior to its predecessors?
The key characteristics of Web 3.0 will lead to many benefits:
- Decentralized: Since intermediaries are removed from the equation, they no longer control user data. This freedom reduces the risk of censorship by governments or corporations and reduces the effectiveness of denial of service (DoS) attacks.
- Improved security: With Web 3.0, powered by decentralization and distributed nature, it will make it less susceptible to hacking and privacy breaches. As it uses encryption technology, Web 3.0 allows users to take complete control and ownership of their data.
- Increased information interconnectivity: As more and more products are connected to the Internet, larger data sets provide algorithms with more information to analyze. This can help them provide more accurate information that meets the specific needs of each user.
- Optimized browser navigation: When using search engines, finding the best results has sometimes been a challenge. However, over the years, they have become better at finding semantically relevant results based on search context and metadata. The result is a more convenient web browsing experience that makes it easy for everyone to find the exact information they need.
- Improved advertising and marketing: No one likes to be bombarded with online ads. However, if the ads are relevant to your needs, they can be useful instead of an annoyance. Web 3.0 aims to improve advertising by leveraging more intelligent AI systems and targeting specific audiences based on consumer data.
- Better customer support: Customer support is essential to the smooth user experience of web sites and applications. However, due to the considerable costs involved, many web services struggle to scale their customer service operations. By using smarter chatbots that can talk to multiple customers simultaneously, users can enjoy a superior experience when working with support agents.
Drawbacks and challenges
- Technology infrastructure: Current technology might be outdated and will then be required to transition towards new technology that would suit to web 3.0 blockchains technology.
- Law regulation in Web 3.0: The legal system needs to be adapted. Data privacy and ownership are the main topics to be legally supervised.
- Environmental challenge: Blockchain technology and machine learning require significant computing power that affect environmentally our planet. Web 3.0 technologies should be improved to become more eco-friendly.
- No guarantee for data security: Cybersecurity principles of Web 2.0 are based on experience. In addition, so far developers have little of it with Web 3.0. It may take time before all the rules and principles of cybersecurity are settled for Web 3.0.
Conclusion
With the massive explosion of available data, websites and apps are evolving into a more immersive web experience. While there is still no concrete definition for Web 3.0, innovations are already in motion. It will redefine how we interact with the digital world and will not only affect individuals but businesses that will need to adapt accordingly their strategy. The transition from web 2.0 to web 3.0 will not happen overnight but what we can say is that it has already started.
https://web3.hashnode.com/a-brief-history-of-web-3#heading-what-is-web-30
https://dzone.com/articles/what-is-web-30
https://appinventiv.com/blog/web-3-0-blockchain-impact-on-businesses/
https://www.simplilearn.com/tutorials/blockchain-tutorial/what-is-web-3-0